Analysis of N-methylpyrrolidine in cefepime hydrochloride by ion chromatography using suppressed conductivity detection with solid-phase extraction pre-treatment
Abstract
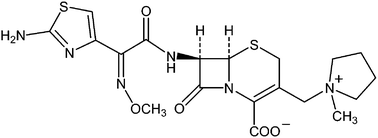
N-Methylpyrrolidine (NMP) is the principal hydrolysis product of cefepime hydrochloride, a β-lactam antibiotic. NMP is limited in cefepime hydrochloride by current regulations to not more than 0.3% w/w. Existing methods for the liquid-phase chromatographic analysis of this impurity fail to separate NMP from the drug substance prior to analysis, with the result that NMP continues to be formed by hydrolysis of cefepime in the final analytical solution. This study proposes a simple, rapid solid-phase extraction procedure that separates NMP from cefepime hydrochloride prior to analysis. NMP was separated from the majority of cefepime in the sample solution using polymeric reverse phase solid-phase extraction. Recovery, precision, sensitivity, linearity and specificity values were adequate to support the use of this method for regulatory purposes. The relative amount of NMP formed in sample extracts processed by solid-phase extraction was at least five times less compared to untreated samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...