Highly-selective electrochemical determination of catechol based on 3-aminophenylboronic acid-3,4,9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes modified electrode
Abstract
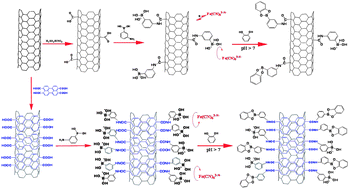
In this paper, a new electrochemical method for the highly-selective determination of catechol (CC) has been fabricated based on the 3-aminophenylboronic acid-3,4,9,10-perylene tetracarboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes (3-APBA–PTCA–CNTs) modified glassy carbon (GC) electrode. The 3-APBA–PTCA–CNTs hybrids and the related electrode were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential pulse voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Due to the highly-selective bonding of 3-APBA with 1,2-diols to form a pinacol ester, the 3-APBA–PTCA–CNTs/GC electrode showed high selectivity for the determination of CC from dihydroxybenzene isomers with a linear response range of 0.5 to 30 μM and a detection limit of 0.1 μM (S/N = 3). Furthermore, the developed 3-APBA–PTCA–CNTs/GC electrode was successfully applied to selectively detect CC in local river water samples with the co-existence of hydroquinone (HQ), CC and resorcinol (RE).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...