Combined SERS and Raman analysis for the identification of red pigments in cross-sections from historic oil paintings†
Abstract
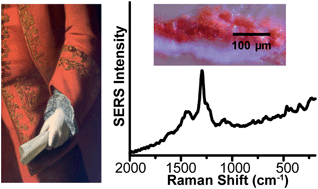
The analysis of paint cross-sections can reveal a remarkable amount of information about the layers and materials in a painting without visibly altering the artwork. Although a variety of analytical approaches are used to detect inorganic pigments as well as organic binders, proteins, and lipids in cross-sections, they do not provide for the unambiguous identification of natural, organic colorants. Here, we develop a novel combined surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), light microscopy, and normal Raman scattering (NRS) approach for the identification of red organic and inorganic pigments in paint cross-sections obtained from historic 18th and 19th century oil paintings. In particular, Ag nanoparticles are directly applied to localized areas of paint cross-sections mounted in polyester resin for SERS analysis of the organic pigments. This combined extractionless non-hydrolysis SERS and NRS approach provides for the definitive identification of carmine lake, madder lake, and vermilion in multiple paint layers. To our knowledge, this study represents the first in situ identification of natural, organic pigments within paint cross-sections from oil paintings. Furthermore, the combination of SERS and normal Raman, with light microscopy provides conservators with a more comprehensive understanding of a painting from a single sample and without the need for sample pretreatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...