A kinetic study of ferrocenium cation decomposition utilizing an integrated electrochemical methodology composed of cyclic voltammetry and amperometry†
Abstract
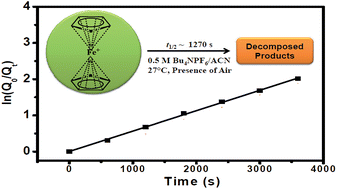
A novel, easy, quick, and inexpensive integrated electrochemical methodology composed of cyclic voltammetry and amperometry has been developed for the determination of the kinetic stability of higher oxidation states for inorganic complexes. In this study, ferrocene and its derivatives have been used as model systems and the corresponding ferrocenium cations were generated in situ during the electrochemical experiments to determine their kinetic stabilities. The study found that the ferrocenium cations decompose following the first-order kinetics at 27 ± 3 °C in the presence of ambient oxygen and water. The half-lives of the ferrocenium, carboxylate ferrocenium, and decamethyl ferrocenium cations were found to be 1.27 × 103, 1.52 × 103, and ≫11.0 × 103 s, respectively, in acetonitrile solvent having a 0.5 M tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate electrolyte. These results are in agreement with the previous reports, i.e. the ferrocenium cation is unstable whereas the decamethyl ferrocenium cation has superior stability. The new methodology has been established by performing various experiments using different concentrations of ferrocene, variable scan rates in cyclic voltammetry, different time periods for amperometry, and in situ spectroelectrochemical experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...