Identification of the sulfoxide functionality in protonated analytes via ion/molecule reactions in linear quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry
Abstract
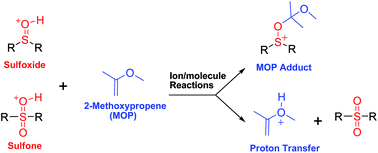
A mass spectrometric method utilizing gas-phase ion/molecule reactions of 2-methoxypropene (MOP) has been developed for the identification of the sulfoxide functionality in protonated analytes in a LQIT mass spectrometer. Protonated sulfoxide analytes react with MOP to yield an abundant addition product (corresponding to 37–99% of the product ions), which is accompanied by a much slower proton transfer. The total efficiency (percent of gas-phase collisions leading to products) of the reaction is moderate (3–14%). A variety of compounds with different functional groups, including sulfone, hydroxylamino, N-oxide, aniline, phenol, keto, ester, amino and hydroxy, were examined to probe the selectivity of this reaction. Most of the protonated compounds with proton affinities lower than that of MOP react mainly via proton transfer to MOP. The formation of adduct-MeOH ions was found to be characteristic for secondary N-hydroxylamines. N-Oxides formed abundant MOP adducts just like sulfoxides, but sulfoxides can be differentiated from N-oxides based on their high reaction efficiencies. The reaction was tested by using the anti-inflammatory drug sulindac (a sulfoxide) and its metabolite sulindac sulfone. The presence of a sulfoxide functionality in the drug but a sulfone functionality in the metabolite was readily demonstrated. The presence of other functionalities in addition to sulfoxide in the analytes was found not to influence the diagnostic reactivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...