Sample preparation for mass spectrometric analysis of human serum N-glycans using hydrophilic interaction chromatography-based solid phase extraction†
Abstract
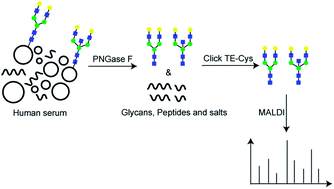
Expression levels of N-linked glycans derived from human serum glycoproteins have been shown to change during the progression of many diseases. Generally, N-glycans released from human serum proteins co-exist with endogenous serum peptides, salts, and other contaminants. Effective removal of these contaminants is essential to obtain the glycan profile of human serum proteins. Here, we developed a sample preparation method for mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of N-linked glycans derived from human serum glycoproteins based on a zwitterionic hydrophilic material named Click TE-Cys. The high hydrophilicity of Click TE-Cys, resulting from its unique surface structure and charge distribution, facilitated removal of co-existing salts and endogenous serum peptides. Furthermore, the present enrichment approach was handled in parallel, thus saving time. Using this method, a total of 47 unique N-glycans released from human serum proteins were identified. The intrabatch and interbatch coefficients of variation for the 47 N-linked glycans were 8.57% ± 0.96% and 9.22% ± 1.03%, respectively. These results demonstrate that the present method is suitable for fast purification of N-linked glycans derived from human serum glycoproteins, and has potential for clinical application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...