Electrochemical monitoring systems of demembranated flagellate algal motility for ATP sensing†
Abstract
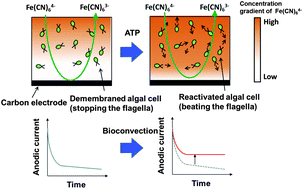
The ATP-induced behavior of the unicellular flagellate alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was recorded as changes in the redox currents for a coexisting redox marker. The ATP concentration was estimated using the presented compact electrochemical system, which is based on monitoring of the motility of the flagellates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...