Examining the effects of self-assembled monolayers on nanoporous gold based amperometric glucose biosensors
Abstract
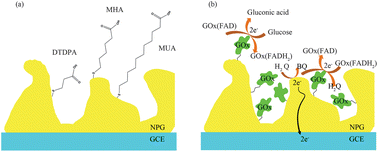
Nanoporous gold (NPG) based biosensors have been constructed by covalently immobilizing glucose oxidase (GOx) onto self-assembled monolayers (SAMs). With p-benzoquinone (BQ) as a mediator, diffusion behavior and amperometric biosensor performance are evaluated by electrochemical characterization. The enzyme modified electrodes are demonstrated to show a thickness-sensitive behavior. Compared with planar polycrystalline gold, the unique porous structure of NPG has also been characterized via an electrochemical surface reconstruction process. Single-crystal gold-like electrochemical behavior on NPG and a comprehensive understanding of its impacts on sensor performance have been proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...