A new nano-optical sensor thin film cadmium sulfide doped in sol–gel matrix for assessment of α-amylase activity in human saliva
Abstract
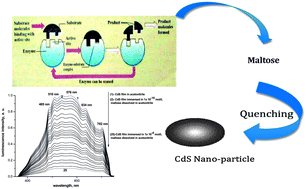
A novel, simple, sensitive and precise spectrofluorimetric method is developed for measuring the activity of the α-amylase enzyme in human saliva. The remarkable quenching of the luminescence intensity at 634 nm of nano CdS doped in a sol–gel matrix by various concentrations of maltose (produced from the reaction of the enzyme with the starch substrate) was successfully used as an optical sensor for the assessment of α-amylase activity. The calibration plot was achieved over the concentration range 4.8 × 10−10 to 1.2 × 10−5 mol L−1 maltose with a correlation coefficient of 0.999 and a detection limit of 5.7 × 10−11 mol L−1. The method was used satisfactorily for assessment of the α-amylase activity in a number of human saliva samples collected from various healthy volunteers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...