Adenosine capped QDs based fluorescent sensor for detection of dopamine with high selectivity and sensitivity†
Abstract
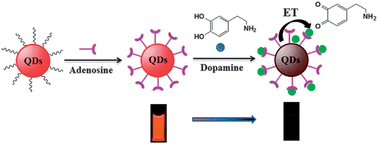
Facile detection of dopamine (DA) in biological samples for diagnostics remains a challenge. This paper reported an effective fluorescent sensor based on adenosine capped CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (A-QDs) for highly sensitive detection of DA in human urine samples. In this assay, adenosine serves as a capping ligand or stabilizer for QDs to render high-quality QDs dispersed in water, and as a receptor for DA to attach DA onto the surface of A-QDs. DA molecules can bind to A-QDs via non-covalent bonding, leading to the fluorescence quenching of A-QDs due to electron transfer. The A-QDs based fluorescence probe showed a limit of detection (LOD) of ca. 29.3 nM for DA detection. This facile method exhibited high selectivity and anti-interference in the presence of amino acid, ascorbic acid (AA), uric acid (UA) and glucide with 100-fold higher concentration in PBS solution. Furthermore, it was also successfully used in the detection of DA in the human urine samples with quantitative recoveries (94.80–103.40%).
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...