A SERS-based pH sensor utilizing 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole functionalized Ag nanoparticles†
Abstract
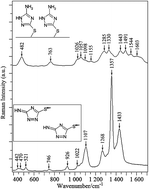
We report the first use of 3-amino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (AMT) to construct a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) based pH nano- and microsensor, utilizing silver nanoparticles. We optimize the procedure of homogenous attachment of colloidal silver to micrometer-sized silica beads via an aminosilane linker. Such micro-carriers are potential optically trappable SERS microprobes. It is demonstrated that the SERS spectrum of AMT is strongly dependent on the pH of the surroundings, as the transformation between two different adsorption modes, upright (A form) and lying flat (B form) orientation, is provoked by pH variation. The possibility of tuning the nanosensor working range by changing the concentration of AMT in the surrounding solution is demonstrated. A strong correlation between the pH response of the nanosensor and the AMT concentration in solution is found to be controlled by the interactions between the surface and solution molecules. In the absence of the AMT monomer, the performance of both the nano- and microsensor is shifted substantially to the strongly acidic pH range, from 1.5 to 2.5 and from 1.0 to 2.0, respectively, which is quite unique even for SERS-based sensors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...