Synthesis of an RGD-grafted oxidized sodium alginate–N-succinyl chitosan hydrogel and an in vitro study of endothelial and osteogenic differentiation†
Abstract
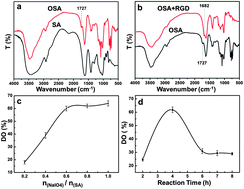
Hydrophilic surfaces for hydrogels as bone tissue engineering scaffolds are not beneficial for the adsorption of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...