One-pot synthesis of PDMAEMA-bound iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetofection†
Abstract
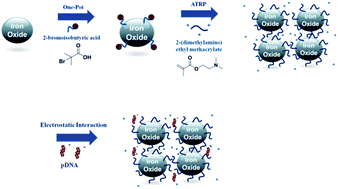
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) have been widely used for multiple biomedical applications. Magnetic-assisted transfection (magnetofection) using SPION is an attractive gene vector candidate. In this work, poly(2-dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-bound iron oxide nanoparticles (IO-PDMAEMA) were generated using a grafting-from approach via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) for use as a gene vector. Preparing an iron oxide-initiator (IO-initiator) is a typical and important step. We designed a simple method to produce an IO-initiator containing bromide groups (IO-Br). The IO-Br was synthesized by reacting iron oxide nanoparticles with 2-bromoisobutyric acid using a one-pot solvothermal method at a high temperature. We optimized IO-PDMAEMA by controlling the PDMAEMA molecular weight, allowing higher gene expression with lower cytotoxicity. The hydrodynamic diameter of IO-Br was 76.7 nm, which increased to 361.7 nm after polymerization. Transversal relaxivity studies suggested that IO-PDMAEMA can be a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetofection efficacy of IO-PDMAEMA/pDNA was measured in HEK 293T cells with or without fetal bovine serum (FBS). The IO-PDMAEMA/pDNA magnetoplexes exhibited remarkably improved gene expression in the presence of a magnetic field and 10% FBS compared with a commercial product, PolyMag/pDNA. No significant cytotoxicity of IO-PDMAEMA/pDNA was observed with different incubation time periods with or without the magnetic field. Confocal laser scanning microscopic images showed that the amount of internalized plasmid DNA increased in the assisted magnetic field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...