Aggregation and de-aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by polyionic drugs: spectrofluorimetric determination of picogram amounts of protamine and heparin drugs in the presence of 1000-fold concentration of major interferences†
Abstract
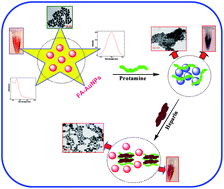
Spectrofluorimetric determination of protamine and heparin was reported using folic acid capped gold nanoparticles (FA-AuNPs) as fluorophore. The FA-AuNPs were synthesized by a wet chemical method and were characterized by UV-visible, photoluminescence, HR-TEM and XRD techniques. They show an absorption maximum at 510 nm and an emission maximum at 780 nm (λex: 510 nm). On addition of 0.05 μg mL−1 protamine, the wine red color of FA-AuNPs turned purple and the absorption maximum attained a red shift. The observed spectral and color changes were attributed to the aggregation of FA-AuNPs and this was confirmed by HR-TEM. Interestingly, on addition of 0.5 μg mL−1 heparin into aggregated FA-AuNPs, the absorption maximum attained a blue shift and the wine red color reverted back. The observed spectral and color changes were due to the strong coordination of protamine with heparin which leads to de-aggregation of AuNPs. Intriguingly, addition of 25 pg mL−1 protamine decreased the emission intensity of FA-AuNPs at 780 nm even in the presence of 1000-fold higher concentrations of Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe2+, SO42−, Cl−, PO43− NO3−, ascorbic acid, glucose interferences and bovine serum albumin interferences. In contrast, addition of 65 pg mL−1 heparin into aggregated FA-AuNPs enhanced their emission intensity at 780 nm in the presence of 1040-fold higher concentrations of the above-mentioned interferences. Based on the increase and decrease in emission intensities, the concentrations of protamine and heparin, respectively, were determined. The lowest detection limits were found to be 4.8 × 10−15 g mL−1 for protamine and 12.6 × 10−15 g mL−1 for heparin (S/N = 3). The present method was successfully applied to determine protamine and heparin in human blood serum samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...