Electrochemiluminescent TiO2/CdS nanocomposites for efficient immunosensing of HepG2 cells†
Abstract
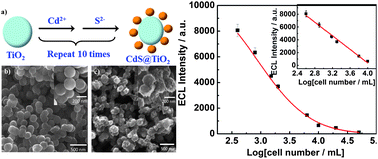
An electrochemiluminescence (ECL) immunosensor for HepG2 cells (human liver hepatocellular carcinoma cells) was fabricated based on CdS-capped TiO2 hybrid nanoparticles. The CdS-capped TiO2 was obtained by immersing TiO2 nanoparticles into separate Cd2+ and S2− solutions successively 10 times. The hybrid nanoparticles have excellent ECL intensity after coating with 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ionic liquid (IL) and 3-aminopropyl-triethoxysilane (APTES). The viscous IL is helpful to immobilize the hybrid nanoparticles on the electrode as well as for the electron transfer from nanoparticles to the electrode, which is advantageous to the ECL immunosensor. APTES was used to attach gold nanoparticles onto the electrode surface. The HepG2 antibodies were then immobilized onto the electrode surface via the interaction between their amine groups and gold nanoparticles. A wide detection range from 400 to 10 000 cells per mL was achieved. The detection limit was determined to be 396 cells per mL. Using HeLa cells as interferences, the excellent selectivity of this sensor has been demonstrated using both confocal fluorescence microscopy and ECL techniques. Due to its good sensitivity, selectivity and stability, the sensor has great potential in medical diagnosis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...