Anticancer loading and controlled release of novel water-compatible magnetic nanomaterials as drug delivery agents, coupled to a computational modeling approach†
Abstract
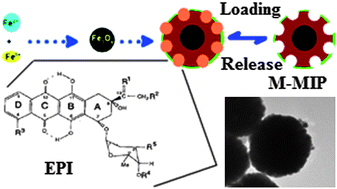
The preparation, characterization and application of novel anticancer “
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Drug Quality Control, Pharmacovigilance China Pharmaceutical University, Ministry of Education, Nanjing 210009, Jiangsu Province, China
E-mail:
jcb315@163.com, dochehua@163.com, pierredramou@yahoo.fr
Fax: +86 025 83271505
Tel: +86 025 83271505
b Department of Pharmacy, Stanford University Medical Center, Palo Alto, CA, USA
c Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Paris V, 4 Avenue de l'Observatoire, 75006 Paris, France
The preparation, characterization and application of novel anticancer “

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
P. Dramou, P. Zuo, H. He, L. A. Pham-Huy, W. Zou, D. Xiao, C. Pham-Huy and T. Ndorbor, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013, 1, 4099 DOI: 10.1039/C3TB20502A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
