Molecularly imprinted fluorescent and colorimetric sensor based on TiO2@Cu(OH)2 nanoparticle autocatalysis for protein recognition
Abstract
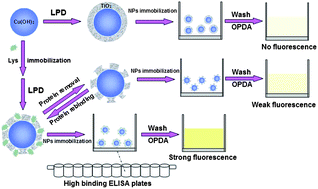
A novel molecular imprinting sensor based on TiO2 sol–gel layers embedding Cu(OH)2 was developed for protein recognition. Protein-imprinted TiO2 layers were prepared by liquid phase deposition (LPD) using lysozyme (Lys) as a template protein. The synthetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles (MIPs) can catalyze o-phenylenediamine (OPDA) oxidation to produce fluorescence and color. Cu(OH)2 played a catalytic role in this reaction. The fluorescence intensity was related to the amount of MIPs, but has nothing to do with the imprinted protein. Taking advantage of this phenomenon, the imprinted protein can be detected using ELISA plates to fixed MIPs by OPDA oxidation. The fluorescence intensity at 568 nm (ex: 350 nm) was found to increase with increasing concentration of Lys. It was found that the limit of detection was 0.001 mg mL−1 with the fluorescent sensor and 0.04 mg mL−1 with the colorimetric sensor under optimized conditions. The results show that the MIPs reached saturated adsorption at 0.2 mg mL−1. Furthermore, the MIPs showed high selectivity compared to other tested proteins. In contrast, the fluorescence change of the non-imprinted TiO2@Cu(OH)2 was only small. The proposed method will be a useful platform for recognition of protein with high sensitivity and specificity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...