Performance loss of aqueous MnO2/carbon supercapacitors at elevated temperature: cycling vs. storage
Abstract
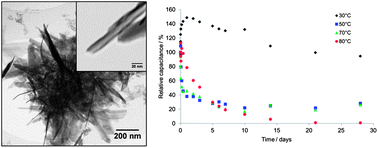
Birnessite MnO2 nanotubes of high specific surface area have been used as one electrode material in supercapacitors with a commercial-carbon-based second electrode ((NH4)2SO4(aq.) electrolyte). Assembled cells have been subjected to full electrochemical testing at temperatures ≤80 °C. At elevated temperatures, specific capacitance as high as 700 F g−1 has been observed. The increase in specific capacitance with temperature has been found to be at a cost to cycling performance. Furthermore, the time spent at elevated temperatures “at rest” has been shown to have a major effect on device lifetime. It has been found that at 80 °C, without cycling, such devices lose all significant capacitance after 21 days. The findings herein are believed to have major implications for transport, storage lifetime and ultimate utilization of such systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...