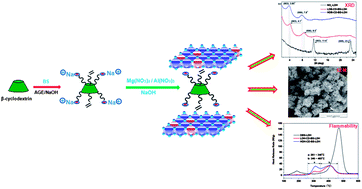
Aiming to develop a multifunctional layered double hydroxide (LDH), a novel bio-based multifunctional anionic modifier, a β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) derivative functionalized with a controllable carbon–carbon double bond (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C) (DB-CD-BS), has been designed, synthesized and used for the in situ synthesis of the functional LDH. The structure of the anionic β-CD-based modifier was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR). The 1H NMR results showed the amount of C
C) (DB-CD-BS), has been designed, synthesized and used for the in situ synthesis of the functional LDH. The structure of the anionic β-CD-based modifier was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR). The 1H NMR results showed the amount of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C in the β-CD-based modifier structure (DB-CD-BS) was controlled by the stoichiometric offset of the reagents. The DB-CD-BS intercalated MgAl–LDHs were prepared via a one step method and characterized by FTIR, Raman, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), elemental analysis (EA), and microscale combustion calorimetry (MCC), respectively. The investigated results illuminated that the DB-CD-BS intercalated LDH showed an increase of the interlayer distance, plate-like morphology with rough edges and good thermal stability. In comparison with the conventional organic modified LDH (DBS–LDH), the MCC results showed DB-CD-BS intercalated LDH (DB-CD-BS–LDH) showed a significant decrease in heat release rate (HRR) and the total heat release (THR) as compared to the corresponding results from DBS–LDH, indicating the DB-CD-BS has low flammability.
C in the β-CD-based modifier structure (DB-CD-BS) was controlled by the stoichiometric offset of the reagents. The DB-CD-BS intercalated MgAl–LDHs were prepared via a one step method and characterized by FTIR, Raman, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), elemental analysis (EA), and microscale combustion calorimetry (MCC), respectively. The investigated results illuminated that the DB-CD-BS intercalated LDH showed an increase of the interlayer distance, plate-like morphology with rough edges and good thermal stability. In comparison with the conventional organic modified LDH (DBS–LDH), the MCC results showed DB-CD-BS intercalated LDH (DB-CD-BS–LDH) showed a significant decrease in heat release rate (HRR) and the total heat release (THR) as compared to the corresponding results from DBS–LDH, indicating the DB-CD-BS has low flammability.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C) (DB-CD-BS), has been designed, synthesized and used for the in situ synthesis of the functional LDH. The structure of the anionic β-CD-based modifier was characterized by
C) (DB-CD-BS), has been designed, synthesized and used for the in situ synthesis of the functional LDH. The structure of the anionic β-CD-based modifier was characterized by ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C in the β-CD-based modifier structure (DB-CD-BS) was controlled by the stoichiometric offset of the reagents. The DB-CD-BS intercalated MgAl–LDHs were prepared via a one step method and characterized by
C in the β-CD-based modifier structure (DB-CD-BS) was controlled by the stoichiometric offset of the reagents. The DB-CD-BS intercalated MgAl–LDHs were prepared via a one step method and characterized by 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...