Polypyrrole-coated α-MoO3 nanobelts with good electrochemical performance as anode materials for aqueous supercapacitors†
Abstract
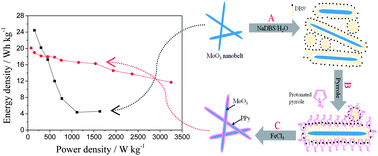
A nanocomposite of molybdenum trioxide (α-MoO3) nanobelts coated with polypyrrole has been fabricated by a simple in situ polymerization route. The structure, morphology and electrochemical performance of the nanocomposite were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and electrochemical measurements. It was found that the polypyrrole acted as a conducting matrix and a coating agent, which effectively improves the conductivity of the MoO3 nanobelts and inhibits the dissolution of molybdenum ions during cycling. The supercapacitor based on the PPy@MoO3 nanocomposite as the anode, activated carbon as the cathode and 0.5 M K2SO4 aqueous solution as the electrolyte exhibits better rate capability as well as excellent cycling performance compared to the virginal MoO3.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...