Synthesis of copper submicro/nanoplates with high stability and their recyclable superior catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction†
Abstract
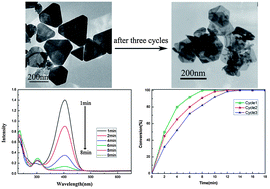
Due to the difficulty in morphology control of planar copper structures, far fewer studies have explored the shape effect on catalytic activity of copper materials. Here, PVP-stabilized copper plates are prepared via the reduction of the Cu(II)–tartrate complex by NaH2PO2 in the presence of PVP under an ambient atmosphere. Based on the systematic studies of varying growth parameters and theoretical simulations, we have discovered the critical factors for synthesizing planar copper crystals. The size of the copper plates can be tuned by adjusting the relative amounts of tartrate, or by changing the types of complex regents with different complexing abilities. The oxidative stability of the resultant copper plates is examined, and their catalytic properties are evaluated. In all cases, the as-prepared submicro/nanoplates show excellent catalytic activity compared with other copper catalysts. Notably, the resultant PVP-stabilized Cu catalyst with submicron size exhibits high stability not only in ambient air, but also toward reduction of p-nitrophenol. It is found that Cu plates are stable and do not lose their structural integrity during reduction catalysis. High stability under the reaction conditions enables the recyclability of the as-fabricated copper plates. We expect catalysts based on copper with plate shapes to meet the increasing demands of industrial applications at reduced costs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...