Polymer electrolyte membranes based on poly(phenylene ether)s with sulfonic acid via long alkyl side chains†
Abstract
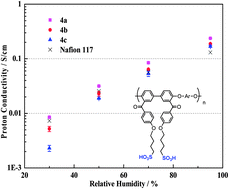
A series of poly(phenylene ether)s with sulfonic acid groups via long alkyl side chains, SPPEs, were successfully prepared as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. The new monomer, bis[4-fluoro-3-(p-methoxylbenzoyl)]biphenyl (BFMBP), containing two pendent methoxyphenyl groups was synthesized by the Friedel–Crafts reaction of 5-chloro-2-fluorobenzoyl chloride with anisole, followed by the nickel-mediated homocoupling reaction. Poly(phenylene ether)s (PPEs) were then successfully obtained by the aromatic nucleophilic substitution polycondensation of BFMBP with dihydroxy-monomers in the presence of potassium carbonate. Sulfonated PPEs (SPPEs) (IEC: 1.96–2.45 mequiv. g−1) could be prepared by the reaction of PPEs containing phenol units with 1,4-butanesultone. By the solution casting method, SPPEs produced transparent membranes with good mechanical properties, and showed good oxidative and dimensional stabilities, and high proton conductivities, e.g., 8.60 × 10−3 S cm−1 under 30% relative humidity at 80 °C, which is higher than that of Nafion 117.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...