Soggy-sand effects in liquid composite electrolytes with mesoporous materials as fillers†
Abstract
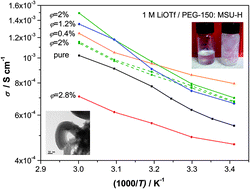
Mesoporous silica particles are used as fillers for soggy-sand electrolytes. Favorable surface chemistry that leads to anion adsorption (as reflected by zeta potential) and conductivity enhancement effects is observed for small volume fractions. More remarkable than the absolute conductivities are the significant transference number increase and the noticeable stationarity of the results for a given preparation. Internally connected pores were shown to contribute to the overall conductivity if not extremely small.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...