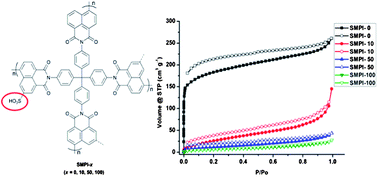
A series of novel microporous polyimides (SMPIs) were synthesized from 4,4′-binaphthyl-1,1′,8,8′-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA), 6,6′-disulfonic-4,4′-binaphthyl-1,1′,8,8′-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (SBTDA) and tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)methane (TAPM). The non-sulfonated SMPI-0 (SMPI-x, where “x” is the molar percent of SBTDA) exhibited a BET surface area of 574 m2 g−1 and a CO2 uptake of 2.53 mmol g−1, while sulfonated samples, i.e. SMPI-10, SMPI-50 and SMPI-100, possessed relatively low BET surface areas (from 23 to 112 m2 g−1) but high CO2 capture capacities (from 2.82 to 3.15 mmol g−1) and CO2/N2 selectivities (from 32 to 57). With the increase of sulfonation degree, the polymers were graded from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. Hydrophobic SMPI-0 and SMPI-10 adsorbed a large amount of non-polar benzene (134.7 wt% for SMPI-0 and 104.7 wt% for SMPI-10) and cyclohexane (42.5 wt% for SMPI-0 and 42.8 wt% for SMPI-10) vapor, whereas hydrophilic SMPI-50 and SMPI-100 adsorbed more polar methanol (68.5 wt% for SMPI-50 and 72.2 wt% for SMPI-100).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...