High performance LiFePO4 microsphere composed of nanofibers with an alcohol-thermal approach
Abstract
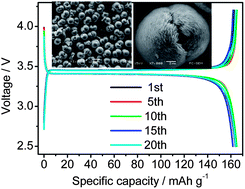
A novel hierarchical nano/microstructure of LiFePO4 microspheres consisting of nanofibers has been synthesized by a solvothermal approach with a mixture of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...