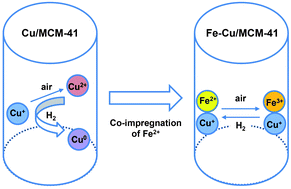
In the present work, a new mesoporous adsorbent containing ferrous/cuprous ionic species (Fe–Cu/MCM-41) has been developed for selective separation of 1-butene/n-butane. Co-impregnation of Fe2+ ions with Cu+ ions within mesopores gives superior 1-butene/n-butane separation ability. Fe–Cu/MCM-41 exhibits much higher heat of adsorption for 1-butene (−23.4 kJ mol−1) compared to that of Cu/MCM-41 (−11.2 kJ mol−1), resulting in a larger adsorption amount of 1-butene over Fe–Cu/MCM-41 (4.4 mmol g−1 at 1 atm) than that over Cu/MCM-41 (2.8 mmol g−1 at 1 atm). The results indicate that Fe–Cu/MCM-41 exhibits superior π-complexation ability for 1-butene than Cu/MCM-41. Moreover, the adsorption ability of Fe–Cu/MCM-41 does not change very much upon H2-treatment at different temperatures in the range of 273 K to 473 K, revealing the excellent hydrogen tolerance of the adsorbent. Physicochemical analyses indicated that the existence of Fe2+ species prevented the oxidation and reduction of Cu+ species during the adsorbent preparation and during the separation process in the presence of a reducing gas such as hydrogen, i.e., the Fe2+ species may act as a kind of redox buffer in the Fe–Cu/MCM-41 adsorbent for improving the chemical stability of Cu+ species that are highly effective for π-complexation with olefin.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...