Fluid-mediated parallel self-assembly of polymeric micro-capsules for liquid encapsulation and release
Abstract
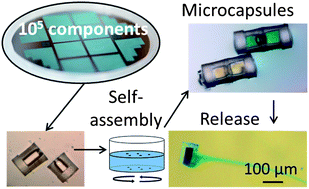
Fluid-mediated self-assembly is one of the most promising routes for assembling and packaging smart microsystems in a scalable and cost-efficient way. In this work the pairwise fluidic self-assembly of 100 μm-sized SU-8 cylinders is studied with respect to two driving mechanisms: capillary forces at the liquid–air interface and the hydrophobic effect while fully immersed in liquid. The pairwise self-assembly is controlled by shape recognition and selective surface functionalization. Surface energy contrast is introduced through oxygen plasma treatment and local deposition of a hydrophobic self-assembled monolayer, respectively leading to face-selective hydrophilic and hydrophobic behavior. When in bulk liquid, after less than a day face-wise self-assembly of more than 650 components is achieved with a yield of up to 97% and with less than 1% of the cylinders assembled incorrectly. This technique is subsequently adopted for self-assembling half-capsules into closed micro-capsules, thereby entrapping a liquid during their self-assembly. The release of the liquid can subsequently be triggered in another medium, as intended for applications involving e.g. chemical reactors, environmental engineering and drug release.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...