Interfacial assembly of lipopeptide surfactants on octyltrimethoxysilane-modified silica surface†
Abstract
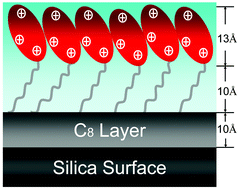
The adsorption of a series of cationic lipopeptide surfactants, C14Kn (where C14 denotes the myristic acyl chain and Kn represents n number of lysine residues) at the hydrophobic solid/water interface has been studied using spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) and neutron reflection (NR). The hydrophobic C8 surface was prepared by grafting a monolayer of octyltrimethoxysilane on the silicon surface. SE was used to follow the dynamic adsorption from these lipopeptide surfactants and the amount was found to undergo a fast increase within the first 2–3 min, followed by a much slower process tending to equilibration in the subsequent 15–20 min. Lipopetide surfactants with n = 1–4 showed similar dynamic features, indicating that the interaction between the acyl chain and the C8 surface is the main driving force for adsorption. The saturation adsorption amount of C14Kn at the C8/water interface was found to be inversely related to the increasing number of Lys residues in the head group due to the increase of steric hindrance and electrostatic repulsion between the head groups. Solution concentration had a significant effect on the initial adsorption rate, similar to the feature observed from nonionic surfactants CmEn. The structure of the adsorbed layers was studied by NR in conjunction with isotopic contrasts. The layer formed by the head groups of C14K1 was 10 Å thick, and those formed by C14K2, C14K3 and C14K4 head groups were all about 13 Å thick. In contrast, the thicknesses of the layers formed by hydrophobic tails of C14K1, C14K2 C14K3, and C14K4 were found to be 17, 13, 10, and 10 Å, respectively, resulting in the steady increase of area per molecule at the interface from 29 ± 2 Å2 for C14K1 to 65 ± 2 Å2 for C14K4. Thus, with an increase in the head group length, the molecules in the adsorbed layer tended to lie down upon adsorption.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...