Cholesterol modulates the fusogenic activity of a membranotropic domain of the FIV glycoprotein gp36†
Abstract
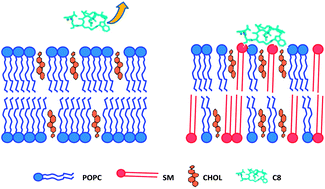
Lipid composition of viral envelopes is usually rich in sphingolipids and cholesterol (CHOL). These components have a stiffening effect on the membrane, thus enhancing the energetic barrier to be overcome for its fusion with the T-cell plasma membrane, a fundamental step of the infection process. In this work, we demonstrate that the octapeptide (C8) corresponding to the Trp770–Ile777 sequence of the Feline Immunodeficiency Virus gp36 is highly effective in inducing the fusion of palmitoyl oleoyl phosphatidylcholine (POPC)/sphingomyelin (SM)/CHOL membranes. We analyze the molecular mechanism of the C8–membrane interactions combining Neutron Reflectivity (NR) and Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) experiments, and molecular dynamics simulations. A strict interplay among the different lipids in the peptide-induced fusion mechanism is highlighted. Since CHOL preferentially locates close to SM, POPC molecules remain relatively free to interact with the peptide, driving its positioning at the membrane interface. Here, C8 comes in contact with CHOL-interacting SM molecules, causing a strong perturbation of acyl chain ordering, which is a necessary condition for membrane fusion. Our findings suggest that CHOL rules, by an indirect mechanism, the activity of viral fusion glycoproteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...