Programmable selectivity of metal–imine bond coordination in subcomponent self-assembly of a primary amine based block copolymer
Abstract
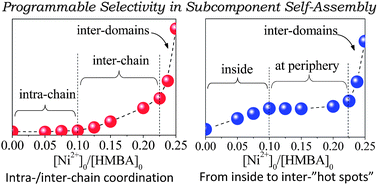
We describe the programmable selectivity of intra-/inter-chain coordination in the subcomponent self-assembly of a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...