Development of cell-impermeable coelenterazine derivatives†
Abstract
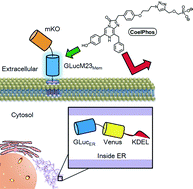
We describe the development of the first cell-membrane impermeable coelenterazine derivative (CoelPhos). CoelPhos was constructed by the alkylation of coelenterazine with a linker containing a terminal anionic phosphonate moiety. The bioluminescence activity of CoelPhos with Gaussia luciferase (GLuc) showed a significantly higher activity in comparison with Renilla luciferase. In imaging studies with living cells, outer membrane bound GLuc was clearly imaged with CoelPhos. On the other hand no signal could be detected with intracellularly localized GLuc, demonstrating the impermeability of this novel coelenterate substrate derivative. CoelPhos has potential utility as a new bioluminogenic tool for the monitoring of dynamic fusion events at the cell–surface interface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...