Investigation of a copper(i) biquinoline complex for application in dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
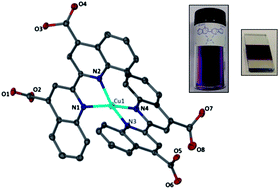
The synthesis, properties and application of a Cu(2,2′-biquinoline-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid)2 complex in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) are described. The complex is electrochemically stable and strongly absorbing with a molar extinction coefficient at λ(max) = 564 nm of 11 700 M−1 cm−1 (in MeOH). Experimental and computational data indicate that the HOMO, LUMO and electronic excited state energy levels are appropriate for functionality in a DSSC. From cyclic voltammetry the HOMO is estimated to be −5.27 eV, as supported by computational work, which locates the HOMO at −5.78 eV. From electrochemical, absorption and emission experiments, the MLCT energy levels are expected to be appropriate for electron injection into the TiO2 conduction band. Our computations support this and locate the key MLCT transition at 563 nm. Despite this, the efficiency in DSSCs is extremely low (<0.1%) suggesting that the dye does not inject excited electrons into the TiO2 conduction band.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...