Highly sensitive formaldehyde sensors based on polyvinylamine modified polyacrylonitrile nanofibers†
Abstract
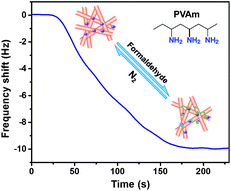
A novel, sensitive, selective, and reproductive formaldehyde sensor has been developed by coating polyvinylamine (PVAm) modified electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibrous membranes on quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) for the first time. Benefiting from the abundant primary amine groups in PVAm, large specific surface area, high porosity and hierarchal structure of PAN nanofibers, and the strong interaction between PVAm molecule and formaldehyde, the as-prepared QCM sensors achieved an extremely low detection limit of 500 ppb in a remarkably short period of time (120 s). Moreover, the sensitivity of the fibrous membranes based sensors are 2.5 times higher than that of flat film-based ones when upon exposure to 500 ppb formaldehyde. Furthermore, the as-prepared QCM sensors possess excellent reproducibility, reversibility, and good selectivity by virtue of the reversible nucleophilic addition reaction between formaldehyde molecule and primary amine group in PVAm. Hence, such promising QCM sensors could not only potentially allow for monitoring gaseous formaldehyde, but also pave a way for designing and development of novel QCM sensing systems based on functionalized nanofibrous membranes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...