Poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) modification of a regenerated cellulose membrane using ATRP method for copper(ii) ion removal
Abstract
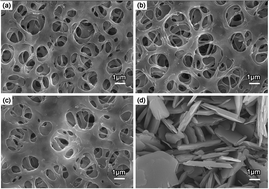
A regenerated cellulose (RC) membrane was functionalized with poly(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) via an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) method to remove copper ions (Cu2+) from aqueous solutions. The presence of PDMAEMA chains was confirmed through attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and grafting degree measurements. The amount of grafted PDMAEMA could be well controlled by changing the polymerization time. The SEM images and solution conductivity of the blank and grafted membranes before and after immersion in a Cu2+ aqueous solution for 12 h showed that the active adsorbent is PDMAEMA only, and not the RC. The adsorption process of PDMAEMA for Cu2+ ion removal was studied in detail by conductivity measurements. Adsorption results indicated that the adsorption capacity increased as the grafting time changed from 5 to 50 minutes. The adsorption capacity remained stable after the grafting time of 30 minutes. The process can be described using the pseudo-second-order model. Isotherm data fitted well to the Langmuir isotherm model, which revealed that 1 g of the grafted PDMAEMA could adsorb 333.33 mg of Cu2+ ions. DMAEMA is expected to be an efficient monomer to modify other materials for the removal of metallic ions from aqueous solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...