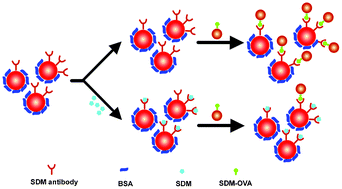
In this study, a simple plasmonic chiral sensor was facilely fabricated based on AuNP oligomers, not aggregations, which were formed by an immuno-driven assembly of two different types of gold nanoparticles. Taking advantage of the high sensitivity of circular dichroism spectroscopy and the high specificity of immuno-recognition, the developed method was used for ultratrace analysis of antibiotics in water. Using SDM as a model antibiotic, the limit of detection reached 0.014 ng mL−1, which is much lower than for other methods. This sensor could be applied to monitor accurate occurrence data of antibiotics in different environments.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...