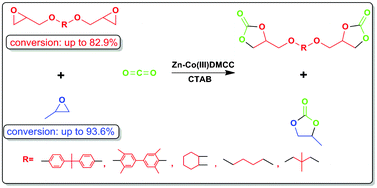
Synthesis of bis(cyclic carbonate) and propylene carbonate via a one-pot coupling reaction of CO2, bisepoxide and propylene oxide†
Abstract
The effective transformation of carbon dioxide (CO2) into valuable products is promising in green and sustainable chemistry. The

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...