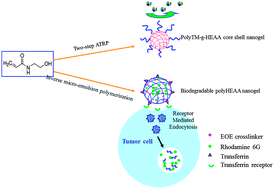
We synthesize and characterize two types of poly(N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide) (polyHEAA)-based nanogels: antifouling poly(2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl trimethyl ammonium-g-N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide) (polyTM-g-HEAA) by a new two-step polymerization method of inverse microemulsion ATRP and surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP), and pH-responsive biodegradable polyHEAA nanogels by the inverse microemulsion free radical polymerization method. PolyTM-g-HEAA nanogels with a core–shell structure by grafting antifouling polyHEAA onto the cationic polyTM core are tested for their antifouling property and stability in fetal bovine serum (FBS) and nanogels-induced cell toxicity. Results show that with the antifouling protection of polyHEAA, polyTM-g-HEAA nanogels significantly improve their long-term stability in FBS up to 7 days by preventing nonspecific protein adsorption, and they also improve cell viability to ∼94% and exhibit almost neglectable cell toxicity. Further, polyHEAA nanogels cross-linked with acid-liable ethylidenebis(oxy-2,1-ethanediyl) ester (EOE) are synthesized, which exhibit both biodegradation and control-release of encapsulated rhodamine 6G (R6G) at acid conditions. Conjugation of transferrin ligands onto R6G-loaded polyHEAA nanogels further enhances cellular uptake efficiency and intracellular drug release for targeting drug delivery. This work demonstrates that polyHEAA-based nanogels with easy synthesis, excellent antifouling property and stability, biodegradability, low toxicity, and pH-responsive intracellular drug release are highly promising for targeted drug delivery systems for biomedical applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...