Assembly–disassembly driven “off–on” fluorescent perylene bisimide probes for detecting and tracking of proteins in living cells†
Abstract
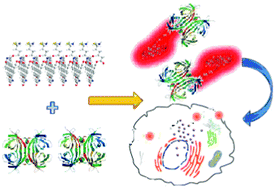
We have developed an assembly–disassembly driven “off–on” fluorescent bioprobe based on amphiphilic perylene bisimide. In aqueous solutions, the amphiphilic probes can form self-assembled

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...