Aqueous synthesis of silver nanoparticles stabilized by cationic cellulose and their catalytic and antibacterial activities†
Abstract
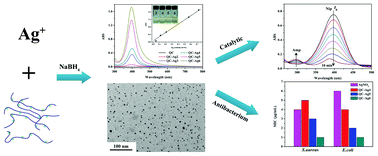
This work studied the synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) in a quaternized cellulose (QC) aqueous solution. In addition, the catalytic and antibacterial activities, as well as the cytotoxicity of QC–Ag NPs are also examined. The results suggest that QC is an ideal protective agent due to the “electrosteric stabilization” provided by its cationic polymer chains. The prepared QC–Ag nanocomposites show high Ag content (93%) and stability, in addition to good solubility in water. QC–Ag NPs are catalytically active in the reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol, and QC is shown to play an important role in the catalytic process, significantly enhancing the catalyst efficiency. On the other hand, the results also show that QC–Ag NPs are nontoxic at concentrations sufficient enough to show good antimicrobial activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...