Mechanistic study of electrochemical treatment of basic green 4 dye with aluminum electrodes through zeta potential, TOC, COD and color measurements, and characterization of residues
Abstract
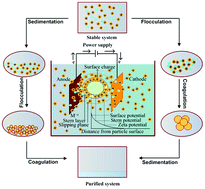
Herein we report a study on the changes in zeta potential during the electrochemical (EC) treatment of basic green 4 (BG) dye solutions. BG is a basic acrylic dye with a triphenylmethane group. It is extensively used in the textile and other industries. This study was conducted in a batch electrochemical reactor using a sacrificial aluminum anode. Zeta potentials were measured with changes in operating variables such as current density (j), initial pH (pH0), and initial dye concentration (C0). The process performance was analyzed in terms of the chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC) and decolorization efficiency along with important cost-related parameters such as electrode and energy consumption. At the optimum conditions, 82.4% COD, 63.5% TOC and 99.4% color removal efficiencies were observed, when C0 = 100 mg L−1, the treatment time was 45 min, with j = 117.64 A m−2 and the initial pH0 = 6.2. The respective electrode and energy consumptions at the optimum conditions were 0.16 kg Al per kg COD removed and 2.48 kW h per kg COD removed. The magnitude of the zeta potential gave an indication regarding the potential stability of the colloidal suspensions of BG dye and aluminum flocs present in the solution over the pH range of 3.2–12.2. It was found that the removal of the cationic dye was maximum when the zeta potential was least negative and that the removal was due to adsorption on neutral aluminum hydroxide. Finally, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), pore size distribution and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) techniques were used to characterize the solid residues obtained during the EC treatment of aqueous solutions with and without BG dye.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...