Ethynylpyrene induces pH-dependent, fluorescence-detectable, reversible DNA condensation and decondensation†
Abstract
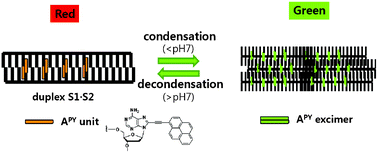
A controllable inducer and signaling system based on ethynylpyrene-containing oligodeoxynucleotides undergoes pH-dependent reversible DNA condensation and decondensation with concomitant changes in fluorescence.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...