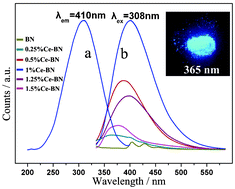
The modification of electronic structure, bandgap energy and photoluminescence properties of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheets has been challenging due to the inherent inertness and chemical stability of h-BN. In the present work, we realized tuning the electronic structure and bandgap energy properties of h-BN nanosheets via a controllable Ce3+ ions doping through a one-step facile thermal chemical reaction route using HBO3, C3H6N6 and Ce(Ac)3·nH2O as reactant precursors. As the Ce3+ ions incorporating content is lower than the critical threshold saturation value of 1.25%, the Ce-doped BN samples show an obvious band gap monotonically narrowing trend from 4.42 eV of pure BN to 3.31 eV for 1.25% Ce-doped BN nanosheets. With incorporation of Ce3+ ions into the lattice of h-BN, the intensity of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) signals closely associated with the nitrogen vacancies in Ce-doped BN samples, displays a decline trend with increasing the concentration of the incorporated Ce3+ ions, suggesting a decrease in the concentration of paramagnetic centers. The introduction of Ce3+ ions can result in the formation of a doping energy level between the conduction and valence bands of BN, and thus shifts the absorption band to the large-wavelength region, corresponding to the bandgap energy narrowing of Ce-doped BN, resulting in a red shift of the absorption edge of the Ce-doped BN samples. The B–N–O–Ce bonding due to the Ce3+ ion doping is responsible for bandgap energy narrowing in the Ce-doped BN materials. As the concentration of the incorporated Ce3+ ions reaches the critical threshold value of 1.25%, no more nitrogen vacancies are available, so the bandgap energy narrowing effect from the Ce3+ ion doping is reduced.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...