Immobilization of radionuclides on poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanofibrous membranes
Abstract
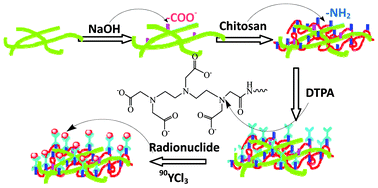
In this work, electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) fibrous membranes were functionalized with radionuclides by surface modification. After the introduction of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...