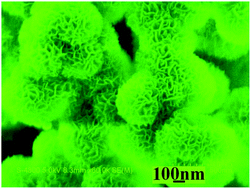
Magnetic Ni/α-Ni(OH)2 porous superstructures with the BET surface area of 114 m2 g−1 have been successfully prepared in one step by a simple mixed solvothermal route in the absence of any surfactant or template at 170 °C for 8 h, employing NiCl2·6H2O and NaBH4 as the reactants, a mixture of ethylene glycol (EG) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) with the volume ratio of 3 : 2 as the solvent. The as-obtained porous superstructures were characterized by various means including X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transformation infrared spectrometry (FTIR) and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS). The magnetic property measurement showed that the saturation magnetization (Ms) and the coercivity of the final product were 6.62 emu g−1 and 141.1 Oe, respectively. Research discovered that some factors could affect the formation of the magnetic porous superstructures, including the original EG/DMF volume ratio, the reaction temperature and the original Ni2+/NaBH4 molar ratio. Importantly, the present porous superstructures presented good capacities for selective adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions from a mixed solution containing Pb2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions. The removal efficiencies for two ions reached 65% and 70% within 50 min, respectively. Simultaneously, the adsorbent could be easily separated from water and reused owing to its magnetism, which exhibit potential application in environmental treatment and protection.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...