Biofunctional micellar nanoparticles from peptide-b-polymer chimeras†
Abstract
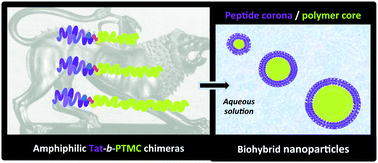
We describe the precision synthesis and characterization of amphiphilic peptide-b-polymer chimeras encoding, at the molecular level, self-assembly properties and biological functions, presently cell membrane penetrating motifs (Tat peptide). Self-assembled micellar nanoparticles obtained from a series of Tat-b-poly(trimethylene carbonate) (Tat-b-PTMC) chimeras with tunable hydrophilic fractions were finely characterized in order to establish chimera–nanoparticle structure relationships. Well-defined nanoparticles with diameters ranging from 22 to 40 nm could be obtained by direct self-assembly in buffer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...