Dilute cationic surfactant-assisted synthesis of polyaniline nanotubes and application as reactive support for various noble metal nanocatalysts
Abstract
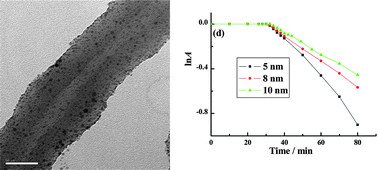
Well-defined and individual polyaniline (PANI) nanotubes have been synthesized by the oxidative polymerization of aniline in dilute solution in the presence of low-concentration cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The role of the surfactant in the formation of the PANI nanostructures was discussed by changing its concentration in the reaction system, and the polymerization processes of low-concentration aniline in the dilute CTAB medium were deduced to explain the formation mechanism of the PANI nanotubes. Furthermore, noble metal (Au, Ag, Pt or Pd) nanoparticles that were supported on the as-synthesized PANI nanotubes have been achieved by utilizing the reactivity of PANI towards noble metal ions. Control over the size of noble metal nanoparticles, typical Au nanoparticles, that were uniformly supported on the surfaces of the PANI nanotubes has been realized by introducing a functional doping acid as the linkage. In addition, PANI nanotube/Au nanoparticle composites were found to serve as effective catalysts to activate the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4NP) in the presence of NaBH4, and the size effects of the catalyst on the catalytic activity were also investigated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...