Photopheresis (extracorporeal photochemotherapy)†
Abstract
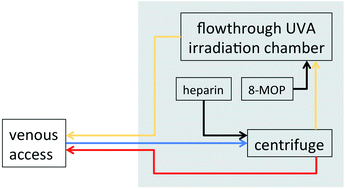
Photopheresis is a form of phototherapy where specialized equipment is used to isolate a leukocyte fraction from the peripheral blood which is then exposed to photoactivated 8-methoxypsoralen and reinfused into the patient. At the time of its invention the treatment was conceptually based on the hypothesis of T cell vaccination, i.e. the observation in experimental studies that exposure of the immune system to physically modified T cell clones leads to a specific inhibition of T cell mediated autoimmunity. Consequently, photopheresis has been tried in a variety of conditions where T cells are thought to have a critical role and has shown clinical efficacy mainly in variants of cutaneous T cell lymphomas, graft-versus-host disease, systemic sclerosis, in solid organ transplant rejection and Crohn's disease. Evidence has accumulated that alterations in
- This article is part of the themed collection: Current topics in photodermatology

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...