Structure–activity relationship studies of the aromatic positions in cyclopentapeptide CXCR4 antagonists†
Abstract
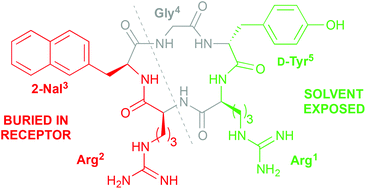
The cyclopentapeptide CXCR4 antagonist FC131 (cyclo(-Arg1-Arg2-2-Nal3-Gly4-D-Tyr5-), 2; 2-Nal = 3-(2-naphthyl)alanine) represents an excellent starting point for development of novel drug-like ligands with therapeutic potential in HIV, cancer, stem-cell mobilization, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases. While the structure–activity relationships for Arg1, Arg2, and Gly4 are well established, less is understood about the roles of the aromatic residues 2-Nal3 and D-Tyr5. Here we report further structure–activity relationship studies of these two positions, which showed that (i) the distal aromatic ring of the 2-Nal3 side chain is required in order to maintain high potency and (ii) replacement of D-Tyr5 with conformationally constrained analogues results in significantly reduced activity. However, a simplified analogue that contained Gly instead of D-Tyr5 was only 13-fold less potent than 2, which means that the D-Tyr5 side chain is dispensable. These findings were rationalized based on molecular docking, and the collective structure–activity data for the cyclopentapeptides suggest that appropriately designed Arg2-2-Nal3 dipeptidomimetics have potential as CXCR4 antagonists.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...