Peptide–LNA oligonucleotide conjugates†
Abstract
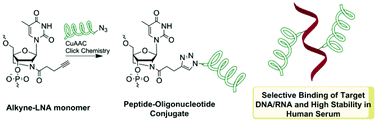
Although peptide–oligonucleotide conjugates (POCs) are well-known for nucleic acids delivery and therapy, reports on internal attachment of peptides to oligonucleotides are limited in number. To develop a convenient route for preparation of internally labeled POCs with improved biomedical properties, peptides were introduced into oligonucleotides via a 2′-alkyne-2′-amino-LNA scaffold. Derivatives of methionine- and leucine-enkephalins were chosen as model peptides of mixed amino acid content, which were singly and doubly incorporated into LNA/DNA strands using highly efficient copper(I)-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) “click” chemistry. DNA/RNA target binding affinity and selectivity of the resulting POCs were improved in comparison to LNA/DNA mixmers and unmodified DNA controls. This clearly demonstrates that internal attachment of peptides to oligonucleotides can significantly improve biomolecular recognition by synthetic nucleic acid analogues. Circular dichroism (CD) measurements showed no distortion of the duplex structure by the incorporated peptide chains while studies in human serum indicated superior stability of the POCs compared to LNA/DNA mixmers and unmodified DNA references. Molecular modeling suggests strong interactions between positively charged regions of the peptides and the negative oligonucleotide backbones which leads to clamping of the peptides in a fixed orientation along the duplexes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...