Benzaldehyde lyase-catalyzed diastereoselective C–C bond formation by simultaneous carboligation and kinetic resolution†
Abstract
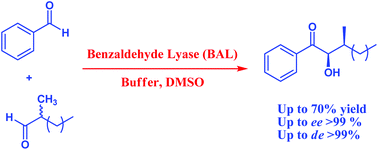
Enzymes create chiral microenvironments that may simultaneously generate several stereogenic centers in the same catalytic cycle, broadening the possibilities of biocatalysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...